Chi-square Test
Definitions
The chi-square test-statistic
where the subscript “c” is the degrees of freedom. “O” is observed value and E is expected value.
Chi-square distribution
The chi-square distribution (or the chi-squared distribution) is a special case of the gamma distribution.
A chi square distribution with n degrees of freedom is equal to a gamma distribution with a = n / 2 and b = 0.5 (or β = 2).
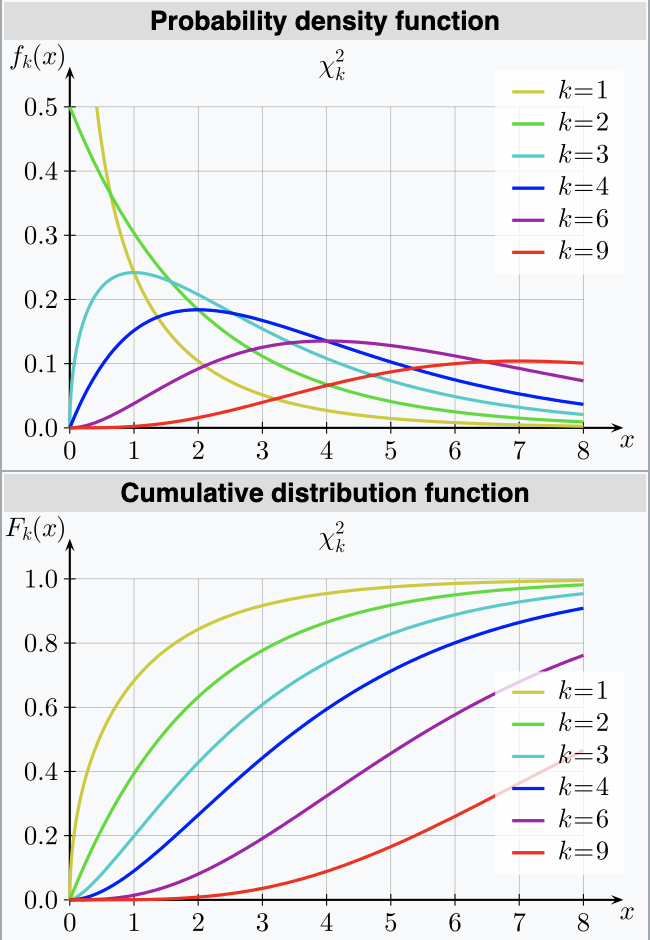
Relationship between $\chi
{ #2}
$ and
You can compare
Applications
Pearson's chi-squared test is used to assess three types of comparison
- A test of goodness of fit => whether an observed frequency distribution differs from a theoretical distribution.
- A test of homogeneity => compares the distribution of counts for two or more groups using the same categorical variable.
- A test of independence => whether observations consisting of measures on two variables, expressed in a contingency table, are independent of each other.
How to determine df
- For a test of goodness-of-fit, df = Cats − Parms, where Cats is the number of observation categories recognized by the model, and Parms is the number of parameters in the model adjusted to make the model best fit the observations: The number of categories reduced by the number of fitted parameters in the distribution.
- For test of homogeneity, df = (Rows − 1)×(Cols − 1), where Rows corresponds to the number of categories (i.e. rows in the associated contingency table), and Cols corresponds the number of independent groups (i.e. columns in the associated contingency table).
- For test of independence, df = (Rows − 1)×(Cols − 1), where in this case, Rows corresponds to number of categories in one variable, and Cols corresponds to number of categories in the second variable.
Rules
- probability of independence
- it does not interpret relationship between variables
- values must be absolute, not percentage
- categories must be mutually exclusive
- minimal 5 observations in each cell