Transformer
What is a transformer?
A transformer is a deep learning model architecture. "Transform" means representation is trained and re-used only by changing downstream layers.
- it is primarily used for natural language processing (NLP) tasks, such as language translation, question-answering, and sentiment analysis.
- key innovation - "Attention is all you need (2017)": self-attention mechanism
- it allows the model to focus on different parts of the input sequence at different times during processing.
- For example, for NLP, self-attention decides which part of a sentence influences which word, by reweighting the Natural Language Processing#Word embeddings with interactions between words.
Types of transformers
encoder only LLM (autoencoding models)
- pretrained using Masked Language Modeling
- it uses bidirectional context = the model understands the full token
- good for:
- sentiment analysis
- names entity recognition
- word classification
- examples
- BERT
decoder only LLM (autoregressive models)
- pretrained using Causal Language Modeling
- it is the majority of recent LLMs
- it uses unidirectional context
- good for:
- text generation
- examples
- GPT
encoder decoder LLM (sequence-to-sequence models)
- pretrained using span corruption (e.g. T5)
- good for:
- translation
- text summarization
- question answering
- examples
- T5
- BERT
Transformer architecture
The original transformer architecture relies on a combination of encoder and decoder
modules. Each encoder and decoder consists of a series of layers, with each layer comprising key components:
- multi-head attention module
- feedforward layer
- residual connection ('Add' layer)
- layer normalization ('Norm' layer)
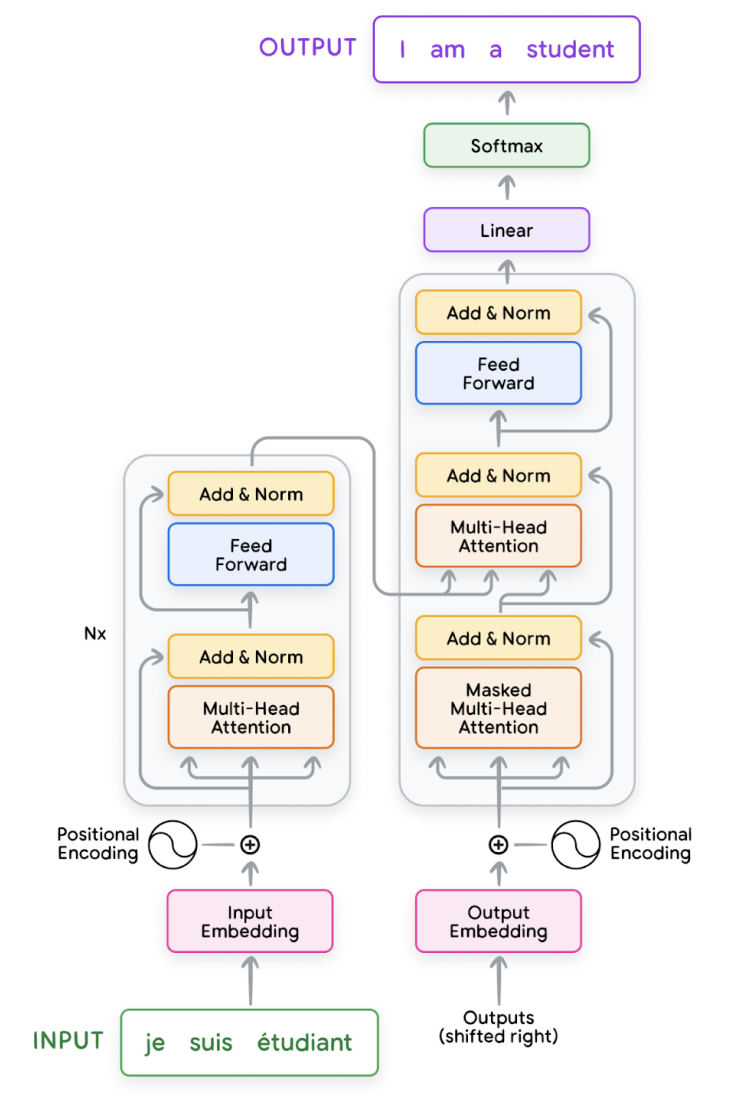
Input embedding
- input embedding represents the meaning of each token in the sentence. This embedding is then fed into
- generating an input embedding involves the following steps
- normalization (optional): standardizes text by removing redundant whitespace, accents, etc
- tokenization: breaks the sentence into words or subwords and maps them to integer token IDs from a vocabulary
- embedding: converts each token ID to its corresponding high-dimensional vector, typically using a lookup table. These can be learned during the training process
- positional encoding: adds information about the position of each token in the sequence to help the transformer understand word order
Multi-head attention
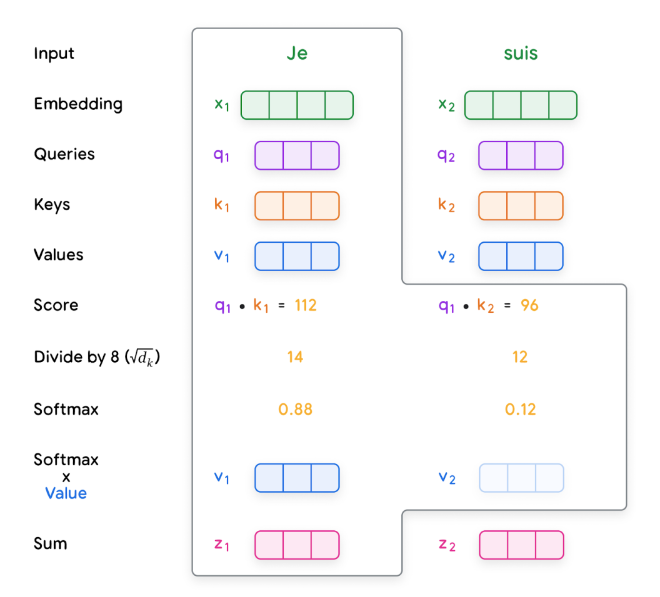
Steps of self-attention
- creating queries, keys, and values:
- Each input embedding is multiplied by three learned weight matrices (Wq, Wk, Wv) to generate query (Q), key (K), and value (V) vectors
- calculating scores:
- scores are calculated to determine how much each word should ‘attend’ to other words
- this is done by taking the dot product of the query vector of one word with the key vectors of all the words in the sequence
- normalization:
- the scores are divided by the square root of the key vector dimension (dk) for stability, then passed through a softmax function to obtain attention weights
- these weights indicate how strongly each word is connected to the others
- weighted values:
- each value vector is multiplied by its corresponding attention weight
- the results are summed up, producing a context-aware representation for each word
Multi-head attention
- Multi-head attention employs multiple sets of Q, K, V weight matrices
- These run in parallel, each ‘head’ potentially focusing on different aspects of the input relationships
Layer normalization & Residual connections
They both contribute to the stability and effectiveness of transformer models.
- Layer normalization
- computes the mean and variance of the activations to normalize the activations in a given layer
- reduces covariate shift and improve gradient flow to yield faster convergence
- Residual connections
- propagate the inputs to the output of one or more layers
- makes the optimization procedure easier to learn and helps deal with vanishing and exploding gradients
Feedforward layer
- typically consists of two linear transformations with a non-linear activation function in between (such as ReLU or GELU)
- add additional non-linearity and complexity into the model’s representations